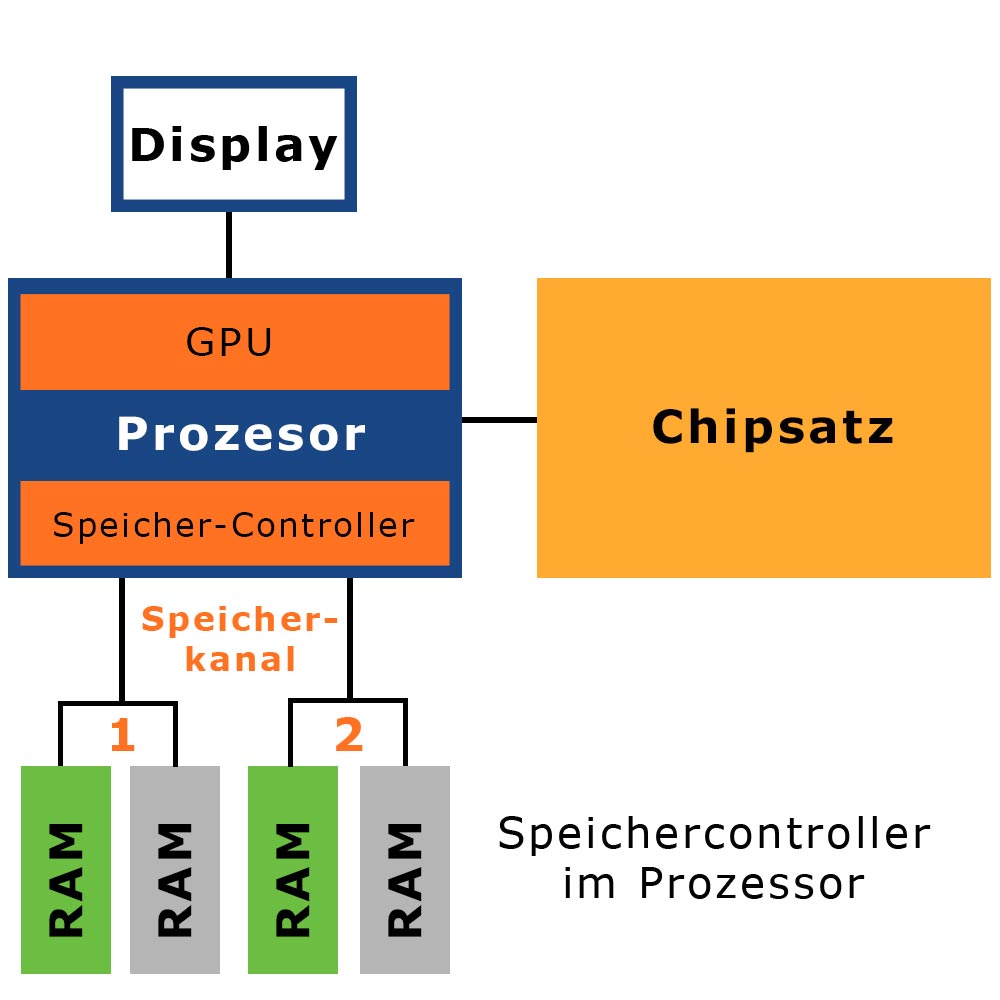
The memory controller addresses the memory modules in the device. Depending on the processor generation, the memory controller is located in the chipset or directly in the CPU.
The memory controller is located in the chipset
In older devices, the memory controller is found in the Northbridge (which is part of the chipset). The Northbridge is connected to the CPU via the Front Side Bus. When the dual-channel mode is activated, only the bandwidth between the memory module and the Northbridge is increased. The bandwidth between the CPU and the Northbridge, however, remains unchanged. Thus, performance improvement is only marginally possible. This technique is based on the principle of memory interleaving.
This applies to all devices that use SDRAM, DDR1, and DDR2 memory modules. However, even with the first systems using DDR3 RAM, there are systems where the memory controller is still located in the Northbridge. For devices with AMD CPUs, this only applies to devices before 2003.

The memory controller is located in the processor
In current devices (AMD from Athlon 64 since 2003; Intel since Intel Pentium 2010/2011), the memory controller is directly in the processor.
Here, the installed RAM is directly addressed by the processor without going through the Northbridge.
Therefore, in these CPUs, the theoretical doubling of the memory bus (data bus) from currently 64 bits to 128 bits in dual-channel mode is possible.