What is an XMP Memory, and what is it used for?
An XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) memory is a specific type of memory designed for use in computers and other electronic devices. The XMP memory is optimized for configuration, allowing it to operate at higher speeds than standard DDR (Double Data Rate) memory.
XMP technology was developed by Intel and enables overclocking of the memory through the BIOS or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). This means that the memory can be operated at higher clock frequencies and latency settings to achieve better performance.
However, it’s important to note that XMP memory is usually more expensive than standard DDR memory and that not all computers and motherboards support XMP. Before purchasing XMP memory, ensure that your motherboard and CPU support XMP.
What are the Key Features of XMP Memory?
XMP memory is not only known for its performance but also for its attractive design. Most XMP memory modules feature striking passive heatsinks, which not only look good but also help keep the memory cool and stable. However, the internal features are what make XMP memory stand out.
Here are some of the key features:
- Increased Clock Rate: XMP memory can operate at a higher clock rate than standard DDR memory.
- Lower Latency: XMP memory generally has lower latency than standard DDR memory.
- Overclocking Profiles: XMP memory has specific overclocking profiles that allow quick and easy optimization of clock rates and latencies.
- Higher Cost: Due to its advanced features and performance, XMP memory is typically more expensive than standard DDR memory.

Intel-Certified XMP Memory: How Does It Work?
Intel’s XMP memory allows overclocking without setting each memory value individually. Voltage, timing values, and CAS latency values are predefined in the memory. These values are permanently stored in the SPD EEPROM on the DIMM board.
The Extreme Memory Profiles (XMP) include not only JEDEC timings in the SPD but also faster Intel XMP values, which are stored in an unused part of the SPD alongside the JEDEC values.

For DDR4 memory, Intel provides the XMP 2.0 standard with two predefined profiles and JEDEC standard settings. DDR5 memory offers the XMP 3.0 standard with three predefined values + 2 user-configurable XMP profiles and JEDEC standard settings.
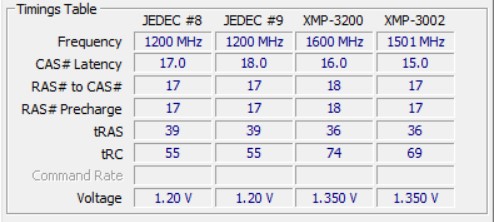
When XMP memory is installed, the system initially boots with the standard JEDEC settings of the memory. If the motherboard, CPU, and all memory modules support the same XMP profile, XMP can be activated in the BIOS or UEFI menu.
In a DDR4-XMP system, two pre-configured profiles are usually available for activation upon enabling XMP.
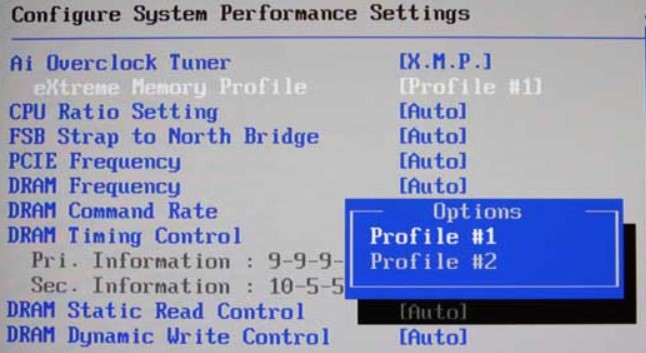
Using predefined XMP parameters for DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 memory allows overclocking without manually setting and testing timing values in the BIOS. Voltage, memory clock, and timings are coordinated in the predefined profiles stored in the SPD EEPROM of the XMP memory. These values are stored as a “package,” allowing profile selection without setting each individual value. This enables overclocking even without detailed knowledge.
Intel XMP Profiles - Benefits and Limitations for Gamers and Office Users
Intel’s XMP profiles enable speeds of up to DDR4 5333 and DDR5 8400 compared to the JEDEC standard of DDR4-25600 (3200MHz) and DDR5-4800/5600MHz. While XMP is irrelevant for office users, it can be interesting for gamers who want to use the available profiles. Note that the motherboard, CPU, and memory must support the same XMP profiles. If you have an AMD CPU, you can use similar features like Asus’ “DOCP,” Gigabyte’s “OCP,” and MSI’s “X-AMP.” Thanks to the predefined memory profiles, overclocking is possible without knowing timing details. The stability is usually better with XMP profiles than with individual overclocking settings. If the motherboard does not support XMP or XMP is not enabled, the memory operates with regular JEDEC timings. Various profiles can be tested, and resetting to the default settings is easy.
Disadvantages of Using Intel XMP Profiles
However, there are some drawbacks: XMP memory is only useful if the motherboard, CPU, and memory support the same XMP profile. Changing the CPU’s frequency and/or voltage beyond Intel specifications can void the processor’s warranty. Activated XMP profile settings can affect system stability. XMP memory is relatively expensive, and the initially high memory frequencies are often quickly matched by increasingly fast JEDEC memory standards. The heatsinks on the DRAMs of XMP memory conceal details, which may cause compatibility issues.
Overall, XMP memory is most appealing to overclocking enthusiasts who should carefully consider its advantages and disadvantages. For office users, XMP is often unnecessary, as system stability is more important than performance.
Note: XMP memory cannot be used with memory modules without the XMP function.
XMP Memory Simplifies Overclocking but Poses Risks to System Security and Processor Warranty
XMP memory, with its predefined profile settings and certification, is an easy way to overclock the CPU, memory, and memory bus on the motherboard. However, a risk to system security remains, as overclocking may void the processor warranty. Additionally, the attractive MHz numbers achievable with XMP overclocking are often surpassed by the rapid development of standard JEDEC memory.
speicher.de currently does not offer XMP memory modules. We prioritize system stability!
